An Introduction to GRASS GIS
Contents
- What is GRASS GIS?
- How to Install GRASS GIS
- Download a Dataset
- Starting GRASS GIS
- Displaying Maps
- Running Modules
- Tutorials
What is GRASS GIS?
The Geographic Resource Analysis Support System (GRASS) is a free and open source geographic information system (GIS). This cross platform GIS runs on Windows, Mac, and Linux. GRASS GIS is released under the GNU General Public License Version 2 or above with source code on GitHub. Go to the GRASS GIS Website to download it, find datasets, find tutorials, and read the documentation. GRASS GIS has more than 500 modules for working with geospatial data. The GRASS GIS tutorials in this course will cover terrain analysis, geomorphometry, map algebra, hydrology, landscape ecology, solar analysis, lidar data analytics, urban modeling, and more.
How to Install GRASS GIS
Download a GRASS GIS installer. Choose a standalone installer for the latest stable release for your operating system - Windows, Mac, or Linux.
Download a Dataset
Download the Natural Earth Dataset for GRASS GIS. This dataset is a GRASS GIS location in the World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84) with global background maps from the Natural Earth collection. Extract the zip archive and move the natural-earth-dataset to your GRASS GIS database directory named grassdata.
Starting GRASS GIS
To start GRASS GIS, you need to set the GRASS GIS database directory, select a location, and then select a mapset. The GRASS GIS database directory will contain locations which in turn contain mapsets. A location is a set of directories containing mapsets with a given coordinate system. Every location has a PERMANENT mapset which contains reference data. Read the GRASS GIS Quickstart to learn more.
| GRASS GIS Startup Screen |
|---|
 |
| GRASS GIS Database Structure |
|---|
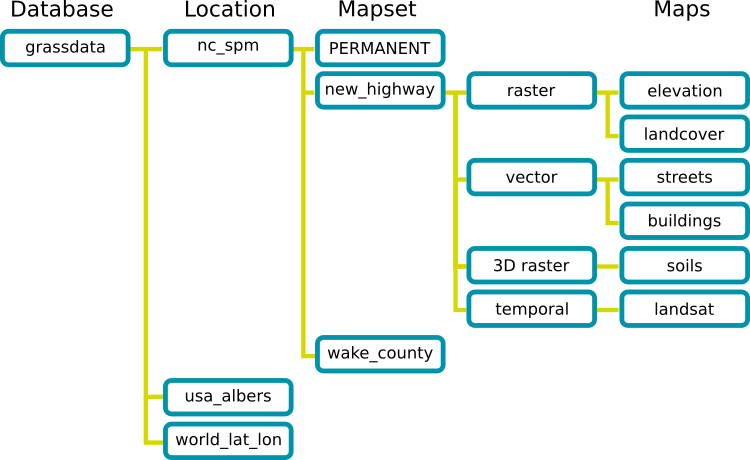 |
A good way of working is to first import reference data
for a given project to the PERMANENT mapset and then
create a new mapset for processing and analyzing the reference data.
Data in the PERMANENT mapset is always accessible from other mapsets.
Working this way means that all your reference data
will be safe and easily accessible in the PERMANENT mapset,
while all new data will be created in the new mapset.
Note that you can create a new location with New button
or download sample datasets as locations with the Download button.
New locations can be created from EPSG codes
for coordinate systems,
from geospatial data such as shapefiles and geotiffs, etc.
For this tutorial download, extract, and move the
Natural Earth Dataset for GRASS GIS
to a directory name grassdata.
This will be your GRASS GIS database directory.
In the GRASS GIS Startup Screen first set your GRASS GIS database directory
by browsing to grassdata.
Then select natural-earth-dataset as your Location.
Select PERMANENT as your mapset.
Then click Start GRASS session.
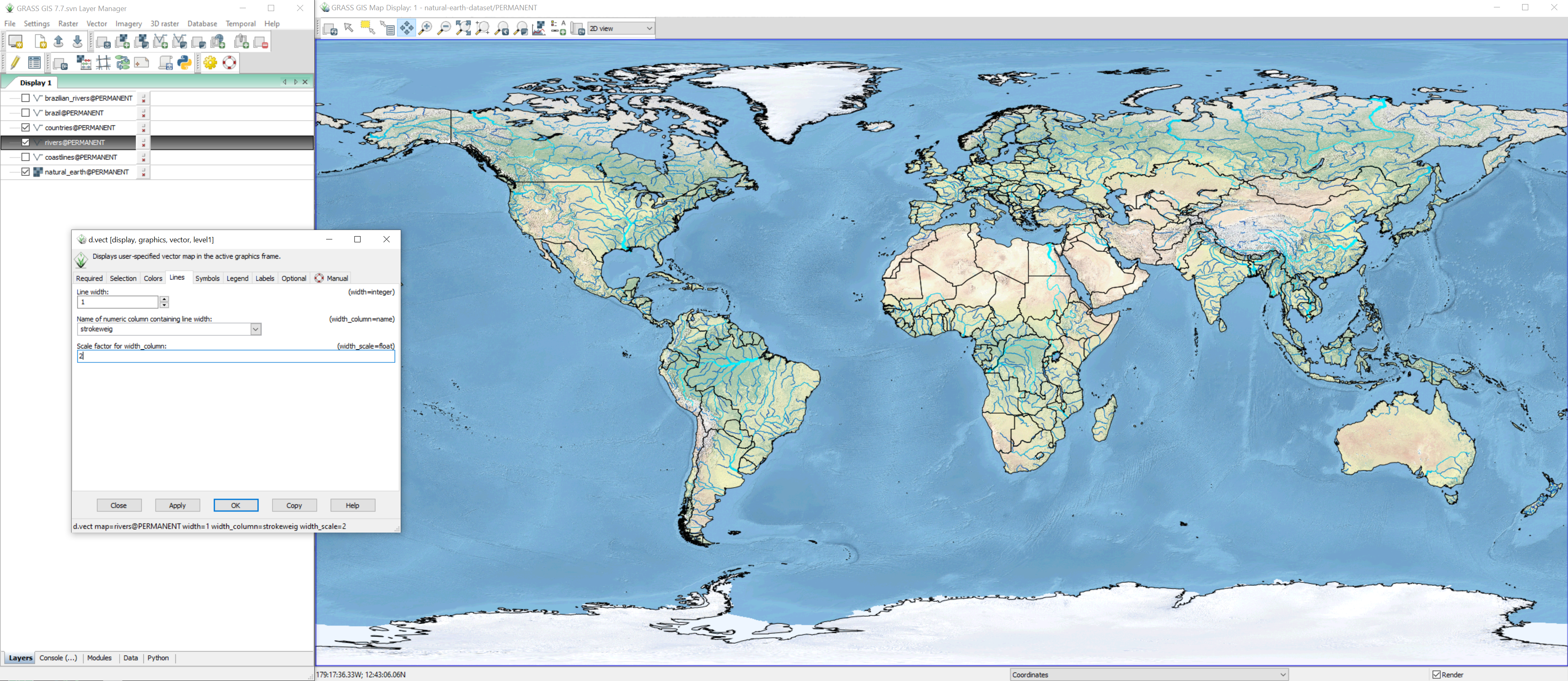
Displaying Maps
Once your GRASS session starts,
the layer manager will be one the left
and the map display will be on the right.
Use the add raster map layer button
or the hotkey Ctrl+Shift+R
to add the natural_earth
raster
to the map display on the right.
This module is called d.rast
with d standing for display and rast for raster.
Then use the add vector map layer button
or the hotkey Ctrl+Shift+V
to add the coastlines vector
to the map display.
This module is called d.vect.
Maps can also be added using the command console.
At the bottom of the layer manager, select the console tab.
In the console, type d.vect
and hit enter to open the add vector dialog.
Or type the command in console:
d.vect map=countries fill_color=none
Use the console to add the countries
vector map
with no fill color.
Then use either add vector map layer dialog or the console
to add the rivers vector with blue linework.
d.vect map=rivers color=blue
| The Rivers of World |
|---|
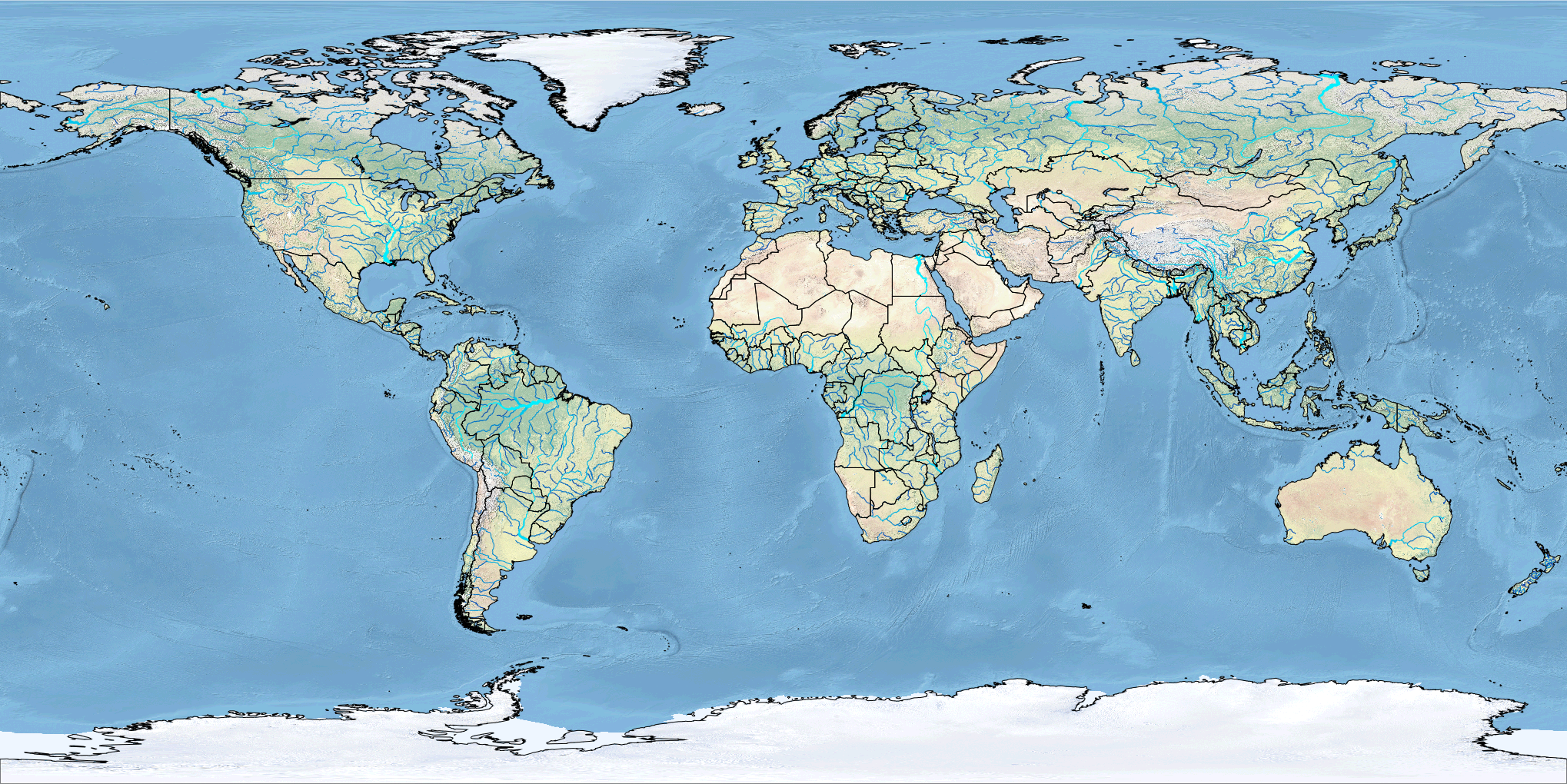 |
Running Modules
In this section of the tutorial,
you will create a new map with rivers for Brazil.
Because you will be creating new data from reference data,
you should first create a new mapset.
Create a new mapset called tutorial by selecting
Settings > GRASS Working Environment > Create New Mapset
from the menu at the top of the layer manager.
Or in the command console type:
g.mapset -c mapset=tutorial
The -c flag enables the creation of a new mapset.
Commands can be run from the menus at the top of the layer manager or from the console or modules tabs at the bottom of the layer manager.
First extract a map of Brazil from the map of countries.
Either use the select vector features button to highlight Brazil
and create a new map layer or run the module
v.extract
in the console:
v.extract input=countries where="ADMIN = 'Brazil'" output=brazil
Zoom to Brazil by right clicking on the map layer
and selecting zoom to selected map.
Then use the module
v.clip
to create a vector map of rivers in Brazil.
Set the input to rivers, the clipping mask to brazil,
and the output to brazilian_rivers.
v.clip input=rivers clip=brazil output=brazilian_rivers
Set a color table for the Brazilian rivers based on their stream order,
i.e. their relative size, using
v.colors.
Right click on the brazilian_rivers layer and select set color table
or run the command v.colors in the console.
Set source values to the attribute table,
set the attribute column to scalerank,
and the color table to water.
v.colors map=brazilian_rivers use=attr column=scalerank color=water
Scale the line weight of the rivers based their stream order
using d.vect.
Set the width column to strokeweig and the width scale to 2.
d.vect map=brazilian_rivers width_column=strokeweig width_scale=2
In the layer manager, uncheck all layers
except natural_earth and brazilian_rivers
to hide the other maps.
Set the computational region to the natural_earth raster map
using the module
g.region.
This will set the resolution of the mask to the same as
the natural_earth raster,
i.e. a cell size of 00:01:12 in degrees minutes seconds.
Then use the module
r.mask
to mask all raster cells outside of Brazil.
A mask limits all raster operations including display
to a boundary.
Simply set the mask to the vector map brazil.
g.region raster=natural_earth
r.mask vector=brazil
| The Rivers of Brazil |
|---|
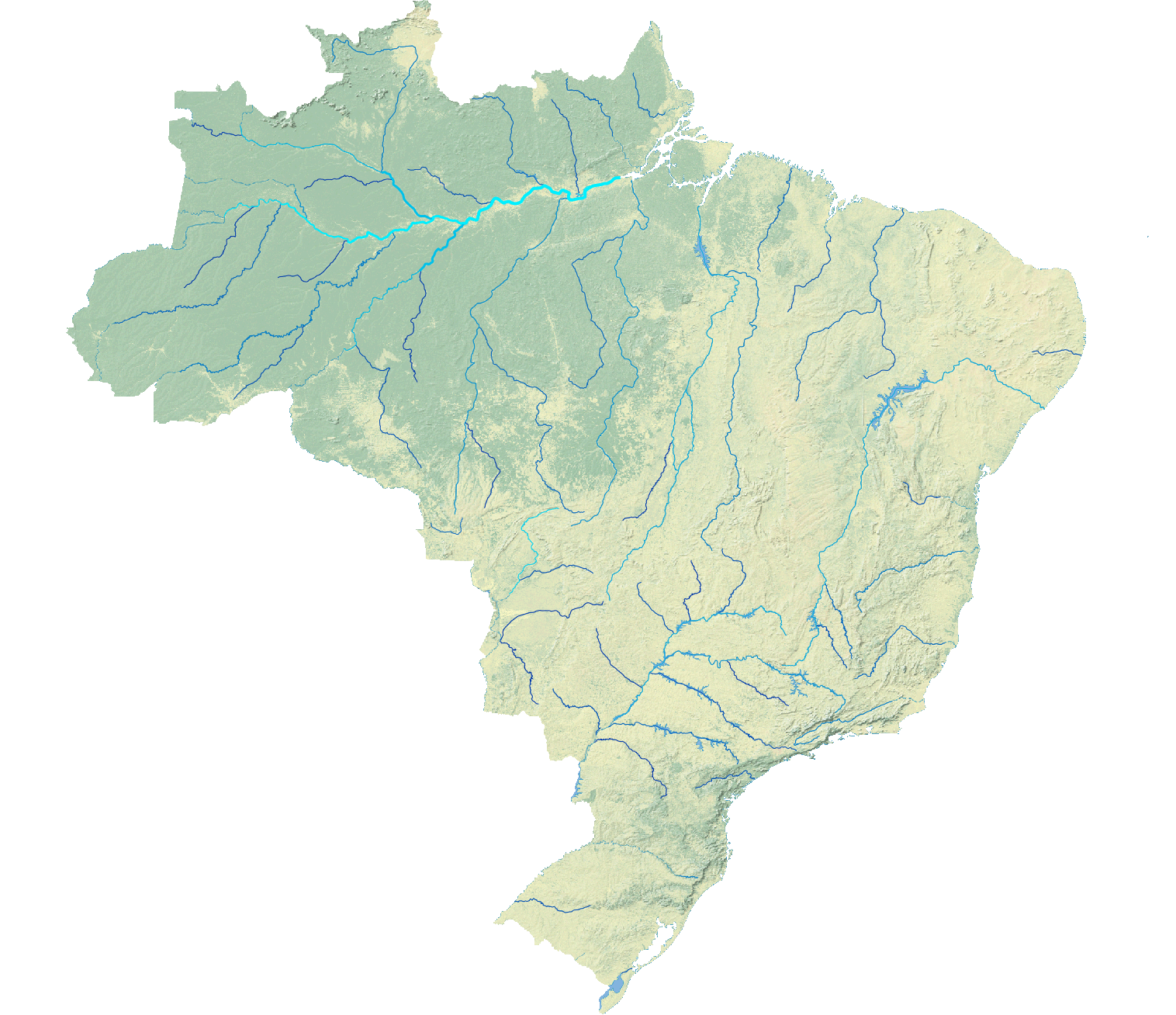 |
To remove a mask run r.mask with the -r flag.
r.mask -r
Save your workspace as a .gxw to save the layout and styling of the maps.
Render your map
as a .png using the save display to file or
as a high resolution .pdf with the cartographic composer
g.gui.psmap.
See the tutorial Cartography in GRASS GIS
for a guide to using the cartographic composer.
Tutorials
Follow these tutorials to learn more about GRASS GIS:
- Vaclav Petras’ Introduction to GRASS GIS + Video
- Paulo van Breugel’s GRASS GIS, QGIS, and R Tutorials