3D random walk with NumPy
tutorial
python
Program a 3D random walk using NumPy
Introduction
Learn how to generate a 3-dimensional random walk in Python with NumPy and render it with either PyVista or Open3D.
Random walk with NumPy
Generate a 3-dimensional random walk with Python’s NumPy library for array programming [1, 2].
# Import libraries
import numpy as np
# Set variables
i = 1000000 # Iterations
mu = 0.0 # Mean
sigma = 0.25 # Standard deviation
scale = 2 # Scale factor
# Instantiate random number generator
rng = np.random.default_rng()
# Generate random steps
u = rng.normal(mu, sigma * scale, i)
v = rng.normal(mu, sigma * scale, i)
w = rng.normal(mu, sigma / scale, i)
# Solve position
x = np.cumsum(u)
y = np.cumsum(v)
z = np.cumsum(w)
# Stack coordinates
xyz = np.column_stack((x, y, z))Render with PyVista
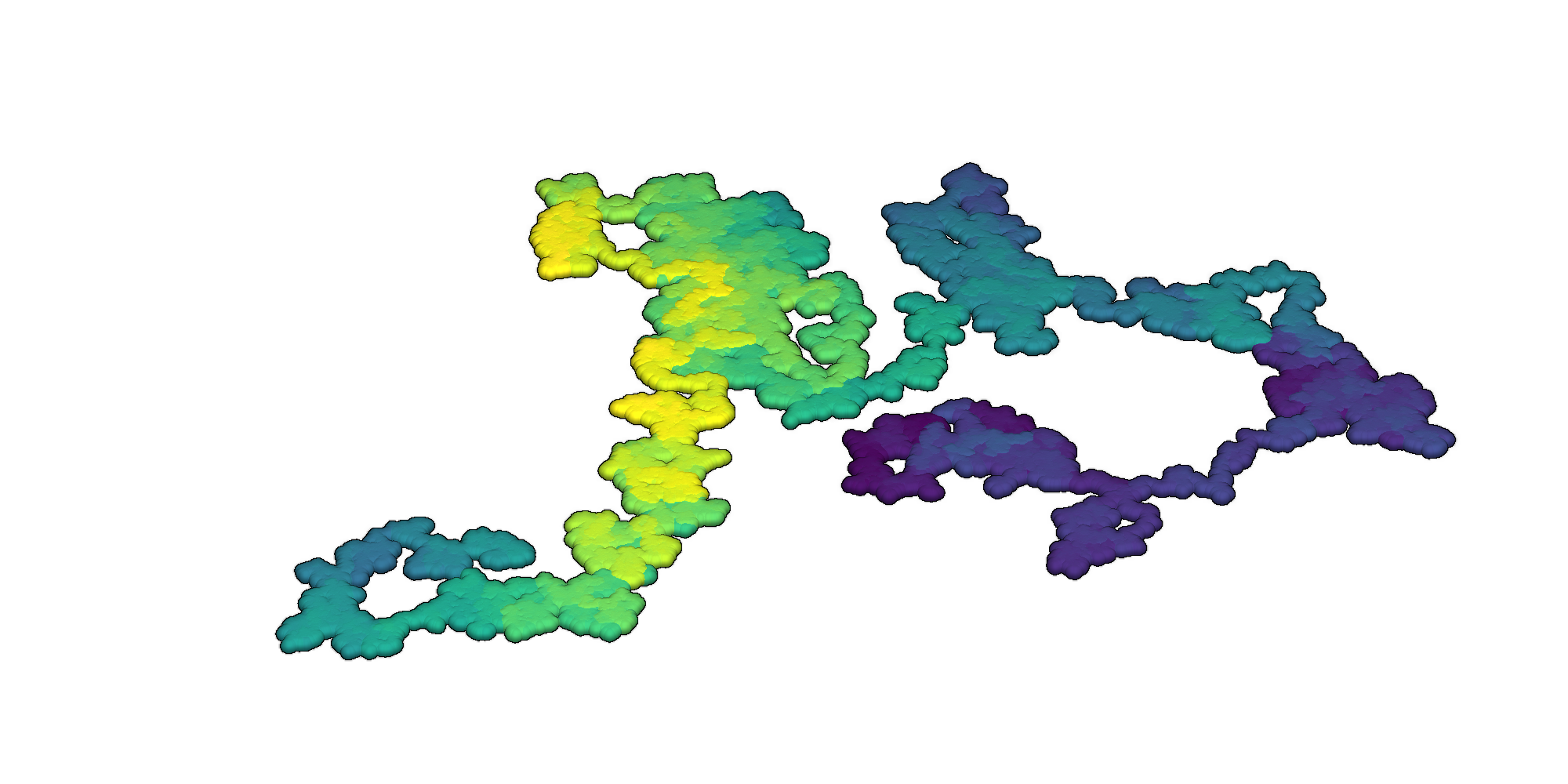
Render an interactive 3D visualization of the random walk with the Python library PyVista [3, 5].
# Import libraries
import pyvista as pv
# Set plot theme
pv.set_plot_theme("document")
# Plot
pv.plot(
xyz,
scalars=z,
render_points_as_spheres=True,
point_size=20,
show_scalar_bar=False,
eye_dome_lighting=True,
ambient=0.6,
diffuse=0.8,
window_size=(2000, 2000)
)
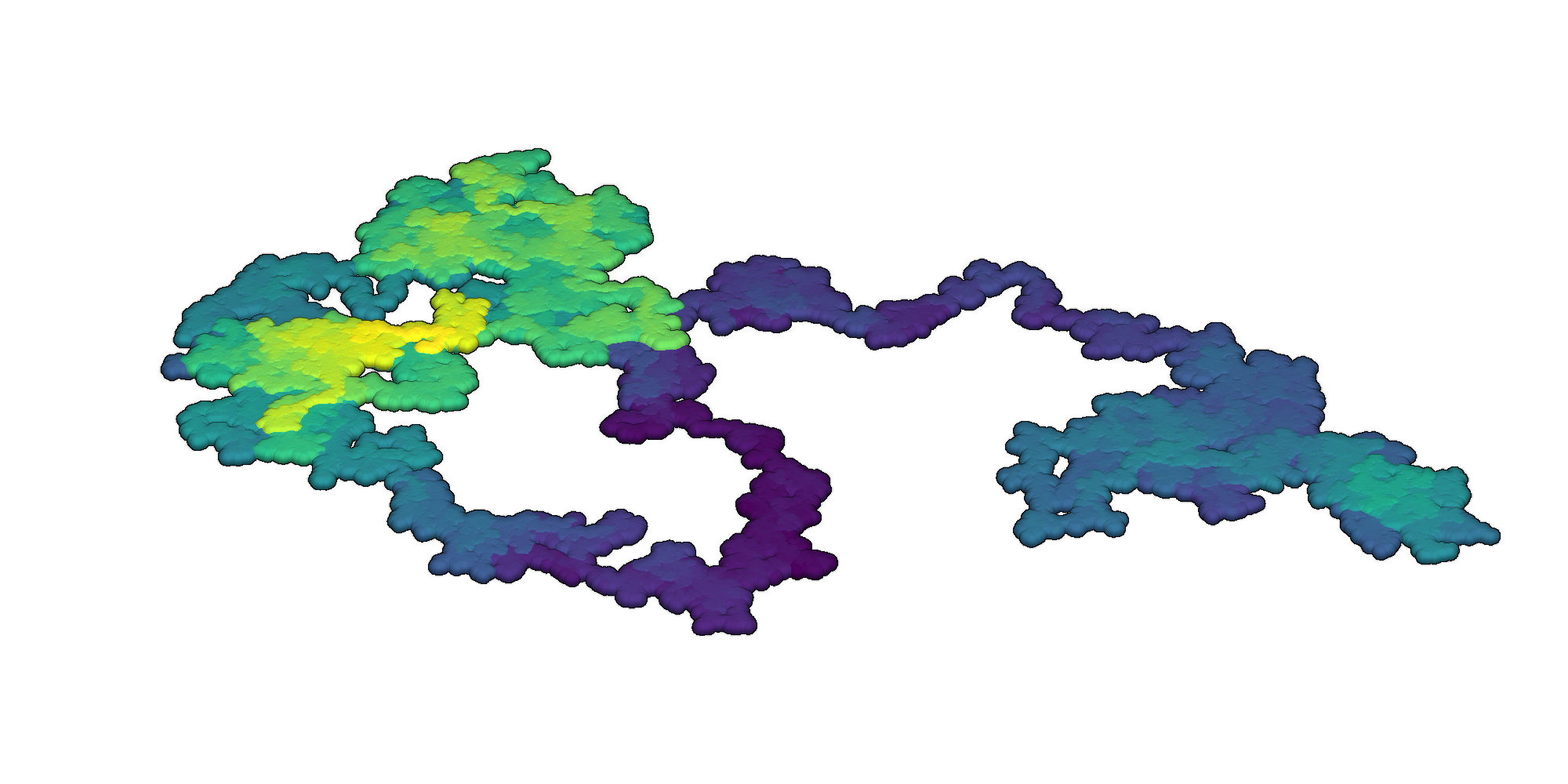
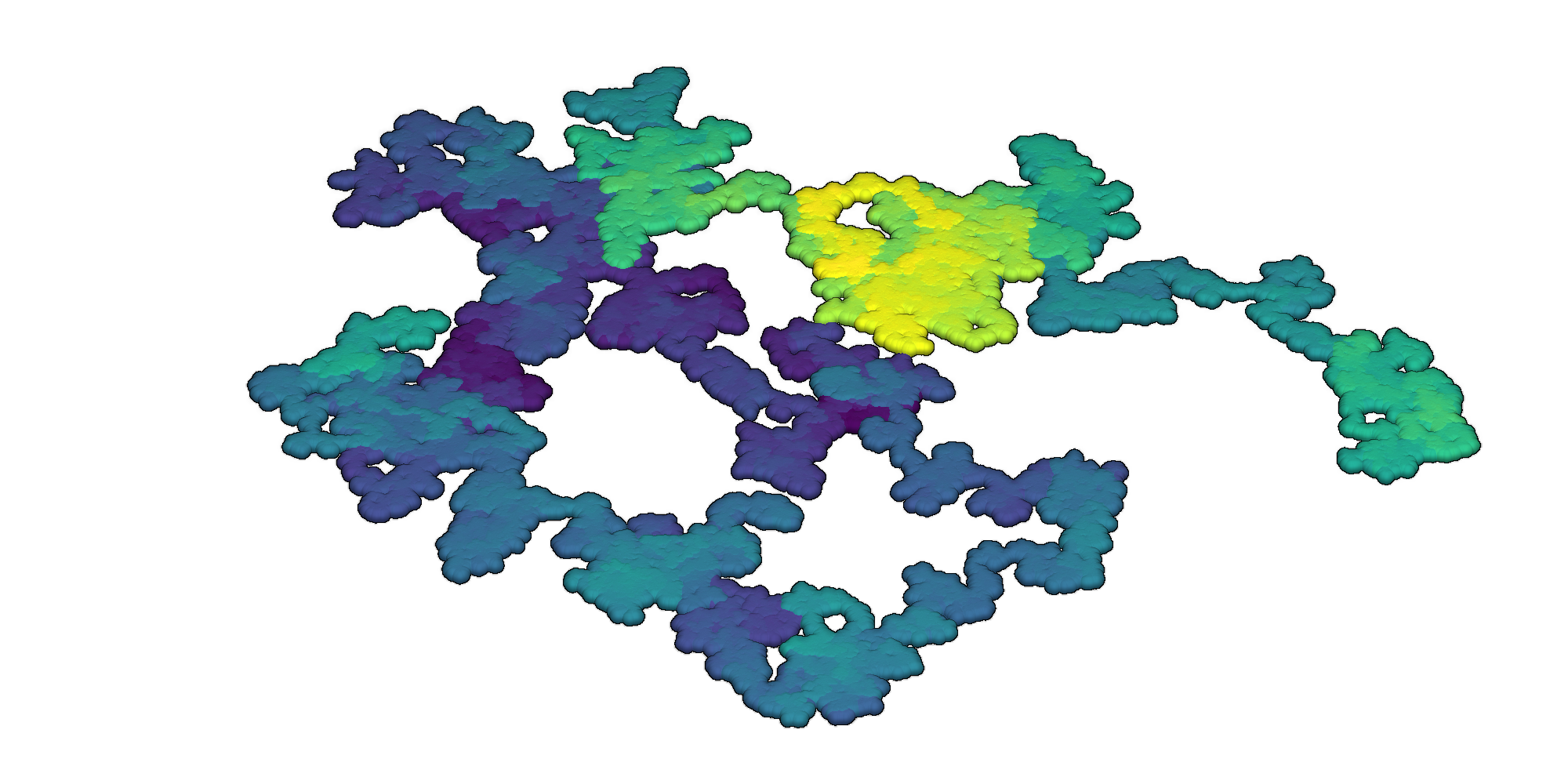
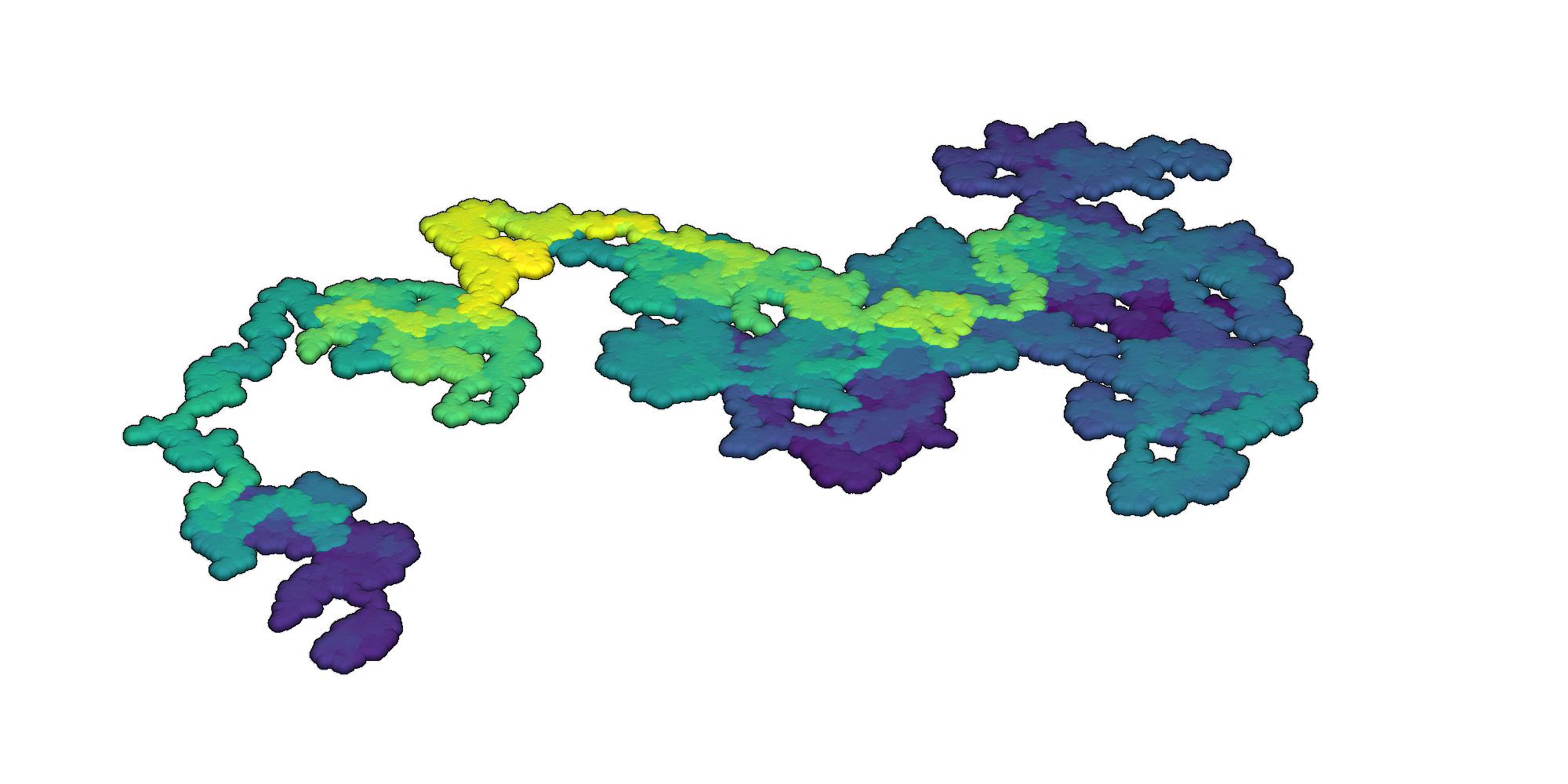
3D random walks rendered with PyVista
Render with Open3D
Render an interactive 3D visualization of the random walk with the Python library Open3D [4, 6].
# Import libraries
import open3d as o3d
import matplotlib.cm as cm
import matplotlib.colors as colors
# Read point cloud
cloud = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
cloud.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(xyz)
# Assign color gradient
colormap = cm.get_cmap("viridis")
normalization = colors.Normalize(vmin=z.min(), vmax=z.max())
normalization = normalization(z)
gradient = colormap(normalization)
gradient = gradient[:, :3]
cloud.colors = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(gradient)
# Render points
o3d.visualization.draw(
[cloud],
point_size=4,
width=2000,
height=2000,
show_skybox=False,
raw_mode=True
)References
[1]
Charles R. Harris, K. Jarrod Millman, Stéfan J. van der Walt, Ralf Gommers, Pauli Virtanen, David Cournapeau, Eric Wieser, Julian Taylor, Sebastian Berg, Nathaniel J. Smith, Robert Kern, Matti Picus, Stephan Hoyer, Marten H. van Kerkwijk, Matthew Brett, Allan Haldane, Jaime Fernández del Río, Mark Wiebe, Pearu Peterson, Pierre Gérard-Marchant, Kevin Sheppard, Tyler Reddy, Warren Weckesser, Hameer Abbasi, Christoph Gohlke, and Travis E. Oliphant. 2020. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 585, 7825 (September 2020), 357–362. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2649-2
[2]
NumPy Developers. 2023. NumPy. Retrieved from https://numpy.org
[3]
Bane Sullivan and Alexander Kaszynski. 2019. PyVista: 3D plotting and mesh analysis through a streamlined interface for the Visualization Toolkit (VTK). Journal of Open Source Software 4, 37 (May 2019), 1450. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.01450
[4]
Open3D Development Team. 2025. Open3D: A modern library for 3D data processing. Retrieved from http://www.open3d.org/
[5]
PyVista Development Team. 2025. PyVista. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.16949653
[6]
Qian-Yi Zhou, Jaesik Park, and Vladlen Koltun. 2018. Open3D: A modern library for 3D data processing. arXiv:1801.09847 (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1801.09847